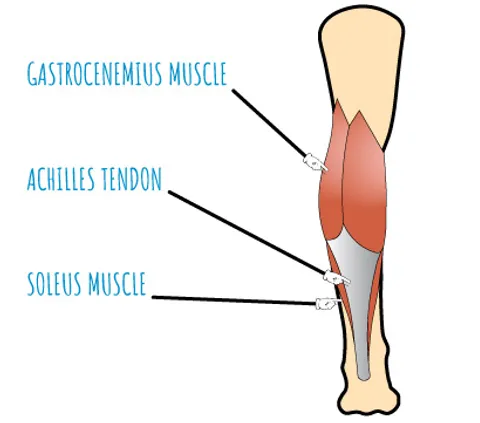
The Achilles tendon, which is comprised of three muscles (gastrocnemius muscle, soleus muscle, and plantaris muscle) is noted to be the largest and one of the strongest tendons in the body, connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone. Children may experience Achilles tendon injuries frequently, due to overuse of the tendon causing tendonitis and tendinosis. In very rare cases, a child may cause actual harm to the Achilles tendon that may include partial or full tears/rupture.
A child with an Achilles tendon injury may complain of common symptoms to the back of the leg, such as; difficulty walking, stiffness, swelling, dull achy pain, difficulty walking and playing sports, and a popping or snapping sound. Although children may state they do not remember a specific cause of injury, Achilles tendon injuries may occur due to various elements. Majority of the time, an accumulation of strain and lack of stretching and proper warm-up or cool-down cause injury to the Achilles tendon. Additionally, training on uneven surfaces without proper conditioning, wearing improper shoe gear, over-exercising or training (over-use), a direct injury, and even having flatfeet may cause Achilles tendon pain and may cause an injury.
Examination
An Achilles tendon injury may be initially discovered by your child’s Pediatrician or athletic trainer. At that point, your child may be referred to a Foot and Ankle specialist or Sports Medicine Physician for further evaluation. The specialist will perform a physical exam in order to rule out tendon injuries, such as a stress test, muscle test, gait exam (watching your child walk), and flexibility test. Examining the Achilles tendon closely and performing specialized tests will help the specialist better understand your child’s condition. Although X-rays may be performed in office, the specialist may order advanced imaging, such as MRI or ultrasound if needed to get a closer look.
Achilles tendonitis may be confused with heel pain (Sever’s disease), which is commonly mistaken and your specialist can help explain the differences to you and tout child.
Treatment
Conservative (Non-Surgical) Treatment
Majority of Achilles tendon injuries may be treated without surgery and your doctor may offer or recommend a plethora of treatment modalities to help get your child healthy. Many of these treatment options involve:
- Physical therapy and exercising
- Activity modification and stretching exercises
- Immobilization
- Appropriate shoe gear
- RICE Therapy [Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation]
- NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatories)
Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatment for Achilles injuries are indicated for traumatic injuries to the Achilles tendon, such as a full rupture of the tendon or failed conservative therapy after several months. The goal of surgical treatment for an Achilles tendon injury is restoring muscle and tendon function and getting back to sports or normal activity level.
Ask your doctor about the many treatments for Achilles tendon injuries and preventative measures you and your child can take.