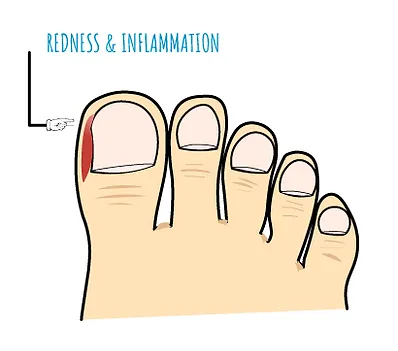
Ingrown toenails are a common condition, in which the corner or side of a toenail grows into the side of the nail fold. Individuals may trim their toenails too short, particularly on the sides of the big toes, which may set the stage for the development of an ingrown toenail. The sides of the nail may curl down and dig into the skin, which causes discomfort and redness. As the ingrown nail progresses, this results in pain, redness, swelling, and sometimes infection, commonly occurring in the big toe.
Prevention – Nail Trimming
The best way to prevent an ingrown toenail from occurring and/or re-occurring is to protect the feet from trauma and to wear shoes that are comfortable and provide adequate room for the toes with little pressure. The toenails should be cut straight across with a clean, sharp nail trimmer without tapering or rounding the corners. Make sure to trim the nails no shorter than the edge of the toe.
Examination
Symptoms of an ingrown toenail may include:
- Swelling of your toe around the nail
- Infection of the tissue around your toenail
- Pain and tenderness in your toe along one or both sides of the nail

Non-Surgical Treatment
It is important to visit your Foot and Ankle Specialist at the immediate onset of an ingrown toenail in order to prevent infection and further pain. If the ingrown nail is recognized early, before infection sets in, a home care regiment may be established to prevent the need for further treatment.
Such treatment modalities include:
- You may take ibuprofen or acetaminophen for pain relief
- Soak the foot in warm water, with Epson salt for 3-4 times daily
- Keep the foot dry during the rest of the day
- Wear comfortable fitting shoes that provide adequate room for the toes
- Trim your toenails straight across, do not curve the nails to match the shape of the front the toe
If there is no improvement in 2-3 days and the toe increases in pain and swelling, call your doctor to schedule an appointment.

Surgical Treatment
If there is excessive inflammation, swelling, pain, and purulent discharge are present, the toenail is most likely infected and should be treated by a physician. You may need to prescribed oral antibiotics and the nail may been to be partially or completely removed, which may be performed in office The doctor can surgically remove a portion of the nail and the nail matrix (a portion of the underlying nail bed), and some of the adjacent soft tissues and even a part of the origin of growth.
Surgery is a valid option for eliminating the nail edge from grow inward into the nail folds as the toenail grows forward. Permanente removal of the nail using a Phenol acid may be advises for children and/or adults with chromic recurrent ingrown toenails. During this procedure, care is taken not to disturb the nail bed, which may result in increase pain.